
Not being able to eat everything you want is indeed a frustrating feeling. Coeliac disease is a nerve-racking digestive disorder that makes your immune system attack your intestine lining every time you eat gluten. This article explains coeliac disease and everything you should know about it.
What Is Coeliac Disease?
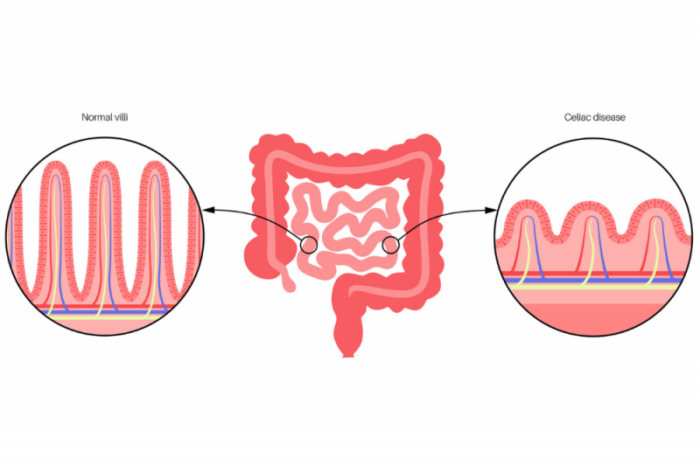
Coeliac disease is an autoimmune digestive disease that makes it hard for the body to absorb gluten. Foods like wheat, barley, rye, and oats have gluten. Consuming gluten-rich food leads to various health issues.
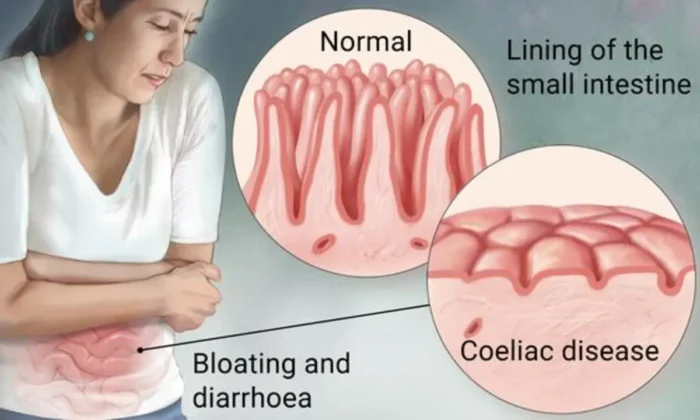
Whenever a person with coeliac disease eats gluten food, the villi (lining of the small intestine) gets damaged. As a result, it becomes difficult to absorb any nutrients properly.
Some other foods that contain gluten are;
- Cake
- Pasta
- Ready-made meals
- Cereals
- Beer
What are the Symptoms of Coeliac Disease?
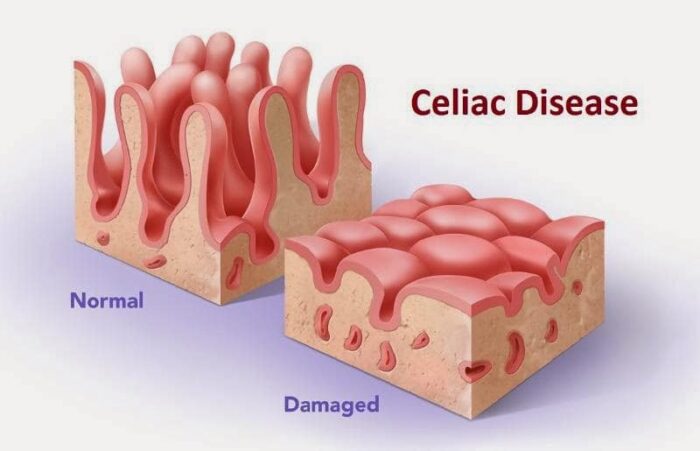
Food containing gluten can trigger inflammatory and other gut responses if you are diagnosed with coeliac disease.
The symptoms of coeliac disease are not prominent. You may have it for years but would confuse it as another health issue. This is why going for a coeliac test is highly recommended if you encounter any of the following symptoms;
- Constant stomach pain
- Nausea
- Anxiety, headache, and depression
- Unexplained weight loss
- Irregular periods
- Bloating and constipation
- Hair loss
- Canker sores
- Bone pain
- Muscle cramps
- Damaged teeth enamel
- Delayed growth
What is a Coeliac Test?
There is no proper way or treatment for coeliac disease. The test is the only way to know if you are diagnosed with coeliac disease. This test examines your blood and looks for antibodies that most people with gluten sensitivity have.
A couple of tests examine your inability to digest gluten food. The standard test for the coeliac test comprises the following steps. Here are the steps for it;
Step # 01 – A doctor will recommend you follow a gluten-rich diet for at least four weeks. During this course, your doctor will perform multiple blood tests, biopsies, and endoscopies by taking your blood sample and tissue sample of the small intestine.
Step # 02 – If the initial blood screening doesn’t rule out any gluten allergy or coeliac disease, your doctor will suggest you stop the gluten intake for four weeks. During this time, your doctor will consider the symptoms – if they are better or worse than with a gluten diet.
Step # 03 – If the symptoms improve when you are gluten-free, you will be advised to reincorporate gluten into your diet slowly. If the symptoms return, you are diagnosed with coeliac disease.
Who Should Go for the Coeliac Test?

Your doctor suggests the coeliac test after carefully evaluating your medical history, family history, genetics, routine, diet, and age.
If you relate to any of these situations, you should undergo coeliac screening.
- If you have persistent mouth ulcers
- Unexplained weight loss
- Personal medical history of autoimmune thyroid disease
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- A down syndrome or turner syndrome child
- Family history of gluten intolerance, cancer, diabetes, autoimmune diseases
- Frequent miscarriages
Final Words
There is no cure for coeliac disease. The only way to lower the effect of this disease is through early detection, constant prevention, and medicated treatment.














