
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a progressive eye condition affecting millions worldwide. It is one of the leading causes of severe and irreversible vision loss globally, accounting for 8.7% of the world’s total blindness.
In 2020, approximately 196 million people experienced AMD, a figure expected to rise to 288 million by 2040. Early detection and prevention strategies are crucial in managing this condition.
Key points:
- Early detection helps slow the condition.
- Nutrition plays a key role in prevention.
- Regular eye exams catch early signs.
- Lifestyle choices impact long-term eye health.
- Supplements support retinal function.
- Smoking increases risk significantly.
Early Warning Signs That Should Not Be Ignored

Changes in eyesight may develop gradually, making early detection difficult without routine checkups. Initially, people may notice blurred central vision, affecting daily activities such as reading or recognizing faces. Straight lines might start appearing wavy, creating distortion that makes driving or household tasks difficult.
Some individuals develop dark or empty spots in their field of view, while others experience muted colors, leading to a dull perception of the environment. Difficulty adjusting to dim lighting may also indicate early signs of macular issues, often ignored until vision loss becomes significant.
The Role of Supplements in Eye Health
Strong retinal function depends on targeted nutrition. Scientific research highlights the benefits of herbal-based supplements in reducing oxidative stress. At ZenLife, decades of innovation have led to patented formulations designed to support long-term ocular health. Their products focus on natural compounds that enhance cellular defense mechanisms against environmental and age-related damage.
These carefully curated herbal blends ensure that the body receives optimal nourishment without unnecessary additives or synthetic compounds, making them an excellent addition to an eye-care routine.
Risk Factors That Increase the Likelihood of Macular Issues

Several factors contribute to macular cell decline. Genetics plays a significant role, with individuals who have a family history facing a higher risk. The likelihood of developing macular problems increases as the body undergoes natural biological changes. Smoking accelerates cell damage, weakening the retinal structure.
Poor dietary habits, particularly those lacking in essential nutrients, deprive the eyes of key antioxidants. Sun exposure damages retinal cells due to harmful ultraviolet rays. High blood pressure reduces circulation to the retina, worsening long-term eye function. Obesity places additional strain on overall vascular health, further limiting nutrient absorption critical for retinal maintenance.
How Nutrition Supports Healthy Retinal Function
A diet rich in essential nutrients serves as a natural defense against macular issues. Studies highlight the importance of antioxidants in slowing cellular decline. Leafy greens such as spinach and kale provide powerful carotenoids, crucial for maintaining healthy retinal pigment.
Fatty fish delivers omega-3 fatty acids, essential for reducing inflammation in ocular tissues. Nuts and seeds contain vitamin E, known for its protective effects against cellular oxidation. Citrus fruits supply vitamin C, enhancing collagen production necessary for retinal strength. Eggs offer a natural source of lutein and zeaxanthin, supporting macular function over time.
Why Regular Eye Exams Are Essential
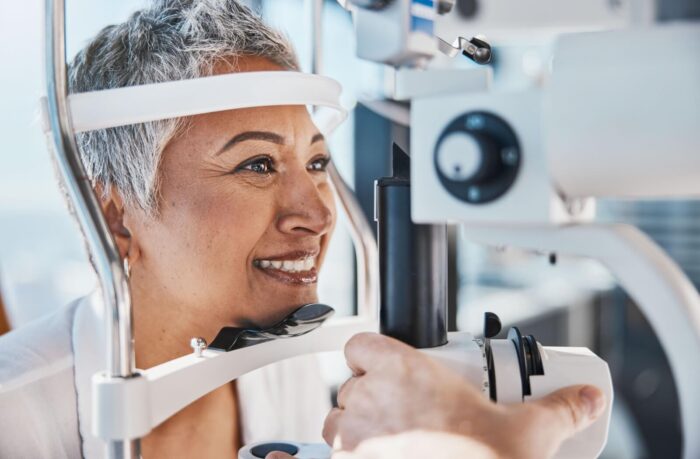
Routine screenings detect changes before major deterioration occurs. Many individuals overlook minor visual disruptions, assuming they result from temporary strain or fatigue. A dilated eye exam provides a comprehensive view of retinal health, allowing specialists to assess structural integrity.
Optical coherence tomography offers advanced imaging, identifying microscopic damage before symptoms manifest. Early medical intervention minimizes progression, ensuring better long-term eye function. Specialists recommend annual checkups for those over 50 or individuals with a family history of macular issues.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Better Long-Term Eye Health
Daily habits influence macular health significantly. Consistent preventive measures can slow or even prevent deterioration in many cases.
- Wear sunglasses ─ High-quality UV-blocking lenses reduce exposure to harmful rays, protecting delicate retinal cells from damage.
- Quit smoking ─ Cigarettes introduce toxic compounds that accelerate oxidative stress, increasing the risk of severe macular decline.
- Maintain a healthy weight ─ Excess weight often leads to systemic inflammation, negatively impacting overall eye function.
- Exercise regularly ─ Physical activity enhances blood flow, ensuring that the eyes receive essential oxygen and nutrients.
- Limit screen time ─ Extended exposure to blue light may cause retinal strain, contributing to premature cellular fatigue.
Medical Treatment Options That Slow Progression

Medical advancements offer solutions for slowing macular deterioration. Anti-VEGF injections target abnormal blood vessel growth, reducing swelling and preserving retinal integrity. Laser therapy addresses specific areas of retinal damage, preventing further progression. AREDS2 supplements provide a clinically studied blend of antioxidants and zinc, formulated to enhance macular resilience against environmental stressors.
Specialists tailor treatments based on individual needs, emphasizing the importance of early intervention.
Preventative Strategies That Make a Difference
The growing prevalence of AMD is driving the AMD market forward, with treatments and research advancing rapidly. The aging population, especially in regions with higher sociodemographic indices, contributes significantly to the increasing burden of AMD. Advances in research, such as recent clinical trials showing improved visual acuity in patients with advanced wet AMD, offer hope for better management and potential cures.
- Eat a balanced diet with nutrient-dense foods ─ Nutritional intake plays a crucial role in preserving macular function over time.
- Get regular eye exams to monitor changes ─ Professional screenings detect early warning signs, enabling timely medical responses.
- Limit exposure to harmful UV light ─ Wearing protective eyewear reduces the risk of sun-induced retinal damage.
- Avoid smoking to reduce oxidative stress ─ Eliminating tobacco products significantly lowers the likelihood of severe deterioration.
- Exercise to promote better circulation ─ Maintaining an active lifestyle ensures proper oxygen delivery to the retina, preventing vascular issues that contribute to degeneration.
- Supplements ─ Consider taking supplements like lutein and zeaxanthin, which may help slow AMD progression.
By adopting these strategies, individuals can reduce their risk of AMD and maintain eye health longer. Early detection and proactive prevention are key to managing this condition effectively.
Conclusion
Age-related macular issues develop gradually, making proactive care essential for preserving eyesight. Nutrition, lifestyle adjustments, and medical interventions play a vital role in slowing progression. Small daily changes make a lasting impact, ensuring better long-term ocular health.














